Nearly a third of all computers are infected with malware
PandaLabs released its annual security report which details an extremely interesting year of data theft, social networking attacks and cyber-warfare.
The most devastating news? 31.98 percent of all computers scanned around the world had malware. With the addition of 2012’s numbers, the grand total of all malware samples in PandaLabs’ database has reached approximately 125 million and researchers estimated that at least 27 million new strains of malware were created in 2012 alone.
Trojans continued to account for most of the new threats, comprising three out of every four new malware strains created in 2012.
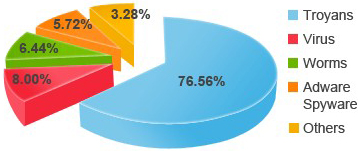
In 2012, Trojans dominated the threat landscape more than ever before. Three out of every four malware infections were caused by Trojans (76.56 percent), up ten points compared to 2011. One of the reasons for this growth was the increased use of exploit kits such as Black Hole, which are capable of exploiting multiple system vulnerabilities to infect computers automatically without user intervention.
Viruses came second (8 percent), whereas worms dropped to third place accounting for 6.44 percent of all infections.

The countries leading the list of most infections are China, South Korea and Taiwan, with 54.89, 54.15 and 42.14 percent of infected computers respectively. On a positive note, the proportion of infected computers around the world decreased significantly. In China, the number of infected computers dropped from 56 percent in 2011 to 54.89 percent in 2012, and in Taiwan, the decrease was even larger (from 52 percent to 42.14 percent).
The countries with the fewest infections are Sweden (20.25 percent of infected PCs), followed by Switzerland (20.35 percent), and Norway (21.03).
Social networking sites play a vital role in the life of Internet users and are extensively covered in the report. Facebook and Twitter continue to be among the most popular social media sites, and are exploited by cyber-crooks to trick users, infect their computers and steal their confidential information. LinkedIn, a tool that is increasingly becoming a key part of job searches, also suffered a massive breach that led to the theft of 6.5 million user passwords.
Ransomware also grabbed headlines in 2012. The ‘Police Virus’ infected hundreds of thousands of computers around the world, using fear and blackmailing techniques to extort money from computer users.
Cyber-crime and social media attacks took the spotlight in 2012 and will continue to do so in 2013. Special care will have to be taken to protect networks against operating system and application vulnerabilities, as it has become increasingly common for cyber-criminals and national intelligence agencies to exploit security flaws to silently compromise systems. In addition, Android users will face a growing number of attacks from cyber-crooks targeting this platform. Cyber-espionage and cyber-war will also be on the rise in a year that presents itself full of challenges in the computer security world.
The complete report is available here.